The field of nutritional and health science continually strives to discover how nutritional compounds influence the body’s defense against pathogens.
Among the myriad of factors influencing immune function, amino acids play a pivotal role, and one such amino acid that has proven beneficial is glutamine. I use Glutamine extensively in my immune-supporting products or products where immune-supporting functionality is needed.
Glutamine, a non-essential amino acid, is not only a crucial building block for proteins but also plays a significant role in various physiological processes, including immune function.
In this article, we will explore the scientific connection between glutamine and immunity, shedding light on the molecular interactions that underlie this relationship.
Glutamine: The Multi-Functional Amino Acid
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the human body and is essential for a myriad of physiological processes.
While it is a non-essential amino acid, meaning the body can synthesise it, certain conditions such as illness, stress, or intense physical activity can increase the demand for glutamine, making it conditionally essential.
In these situations, the body may require additional glutamine from dietary sources or supplements.
Immune Cells and Glutamine
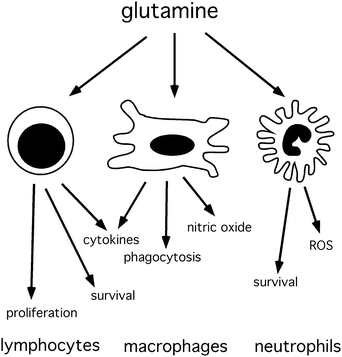
Immune cells, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, are highly metabolically active and require a constant supply of energy and building blocks to carry out their functions effectively.
Glutamine serves as a critical substrate for these immune cells, participating in various metabolic pathways that support their proliferation, survival, and function. Glutamine works on the immune cells in the following ways.
- Energy Supply: Immune cells, especially rapidly dividing ones, heavily rely on energy from glutamine pathway to sustain their heightened metabolic demands during an immune response.
- Antioxidant Defence: Glutamine contributes to the synthesis of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant. Immune cells utilise glutathione to protect themselves from oxidative stress induced by the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which are used by immune cells to destroy pathogens.
Glutamine and Gut Health: Bridging the Gap
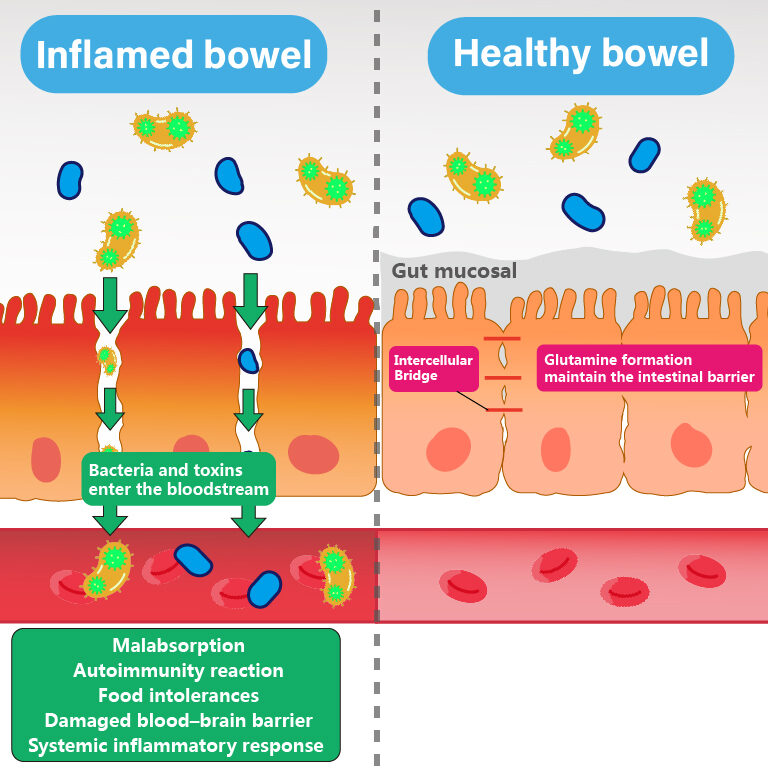
In addition to its role in supporting immune cells, glutamine also plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health, which is intimately connected to immune function.
- Tight Junction Maintenance: Glutamine is essential for the maintenance of tight junction proteins in the intestinal lining. These proteins play a crucial role in forming a barrier that regulates the passage of molecules across the gut lining, preventing the entry of harmful pathogens.
- Mucin Production: Glutamine stimulates the production of mucin, a protein that forms a protective layer on the intestinal surface. Mucins play a vital role in trapping pathogens, preventing them from sticking to the intestinal lining and causing harm, and facilitating their removal from the body.
How to Use Glutamine Supplements
In practical terms, incorporating glutamine into your diet can be achieved through dietary sources or supplements.
Foods rich in glutamine include beef, poultry, fish, dairy products, and certain plant-based sources like beans and spinach. Alternatively, glutamine supplements are available for those with increased demand or specific dietary restrictions.
For individuals seeking targeted support for immune health, formulations that include glutamine supplements can be beneficial.
The optimal dosage of glutamine can vary based on individual factors such as age, health status, and specific health goals. For general immune support, dosages typically range from 5 to 20 grams per day. It is advisable to start with lower doses and gradually increase while monitoring individual tolerance.
For athletes undergoing intense training or individuals facing conditions that increase glutamine demand, higher doses within the range of 20 to 30 grams per day might be considered, although this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
As someone passionate about immune health, I include glutamine supplements in my immune formulations to enhance their effectiveness. These formulations are designed to provide a balanced combination of nutrients, including glutamine, to support the immune system’s robust functioning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glutamine emerges as a key player in the intricate network of factors influencing immune function and gut health. Its roles in energy production, nucleotide synthesis, antioxidant defense, and the maintenance of gut integrity highlight the multi-faceted contributions of this amino acid to overall health. As scientific understanding deepens, the potential therapeutic applications of glutamine supplements in modulating immune responses and supporting gut health, especially in well-designed formulations, may offer new avenues for interventions in various clinical scenarios.

To view my Professional Profile on LinkedIn: please click here
To see my latest product creations: www.bioteenhealth.com
To view my Scientific Publications on PubMed: please click here
To get in touch, please write to: info@supplementscientist.com
Follow supplementscientist.com on Facebook: please click here
Medical disclaimer
The information presented on this website is intended for adults 18 or over. Its aim is purely educational and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult a medical or health professional before you begin any program related to exercise, nutrition, or supplementation especially if you have a medical condition. If you consume any product mentioned on our site, you do so on your own free will, and you knowingly and voluntarily accept the risks. © 2023. Supplementscientist.com







Leave a Reply