I am a big believer in the immense power of amino acids and I never miss an opportunity to create products with these remarkable molecules.
One of the amino acids that I believe in is betaine. I have incorporated Betaine into products that are designed to optimise health, mental and physical well-being, and athletic performance.
These products include cognitive enhancers, preworkout supplements, intra-exercise sports drinks and in a near future several health-supporting formulations will hit the market in which I will include betaine.
Betaine is used heavily in animal nutrition and I have also included it in animal feed formulations.
This article dives into the world of betaine, covering its definition, food sources, supplemental forms, its involvement in various reactions, and its key applications in promoting health and enhancing sports performance.
What is Betaine?
Betaine, also known as trimethylglycine (TMG), is an organic compound derived from the amino acid glycine.
It is found in various plants, microorganisms, and marine animals. Structurally, betaine possesses three methyl groups (-CH3), which contribute to its unique characteristics and functional versatility.

Food Sources and Supplemental Forms
Betaine is naturally present in several food sources, albeit in varying concentrations. Some notable dietary sources of betaine include beets, spinach, wheat bran, quinoa, and seafood such as shrimp, crab, and fish.
However, the amounts of betaine obtained through regular dietary intake may not always be sufficient for specific health or performance goals.
In such cases, betaine can also be obtained through supplemental forms.

Craig, S.A. (2004). Betaine in human nutrition. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 80(3), pp.539–549.
The main forms of supplemental betaine are betaine anhydrous, betaine hydrochloride. I formulate with both of them, depending on the end product.
Key Reactions and Functions of Betaine
A. Betaine as an “Osmolyte”
One of the key roles of betaine is its function as an osmolyte.
Osmolytes are compounds that help organisms maintain their cellular structure and integrity during times of environmental stresses such as extreme temperatures, and dehydration.
Betaine accumulates in cells and this helps cells attract water.
The maintenance of cellular water content aids in maintaining the structure of the cells by preventing shrinkage, its function as well as the stability of various protein structures in cells under challenging conditions.
One situation in humans where betaine functions as an osmolyte is during dehydration.
When the body undergoes dehydration, whether due to inadequate fluid intake, excessive sweating, or other factors, cells can lose water and face osmotic stress and the regulation of betaine content
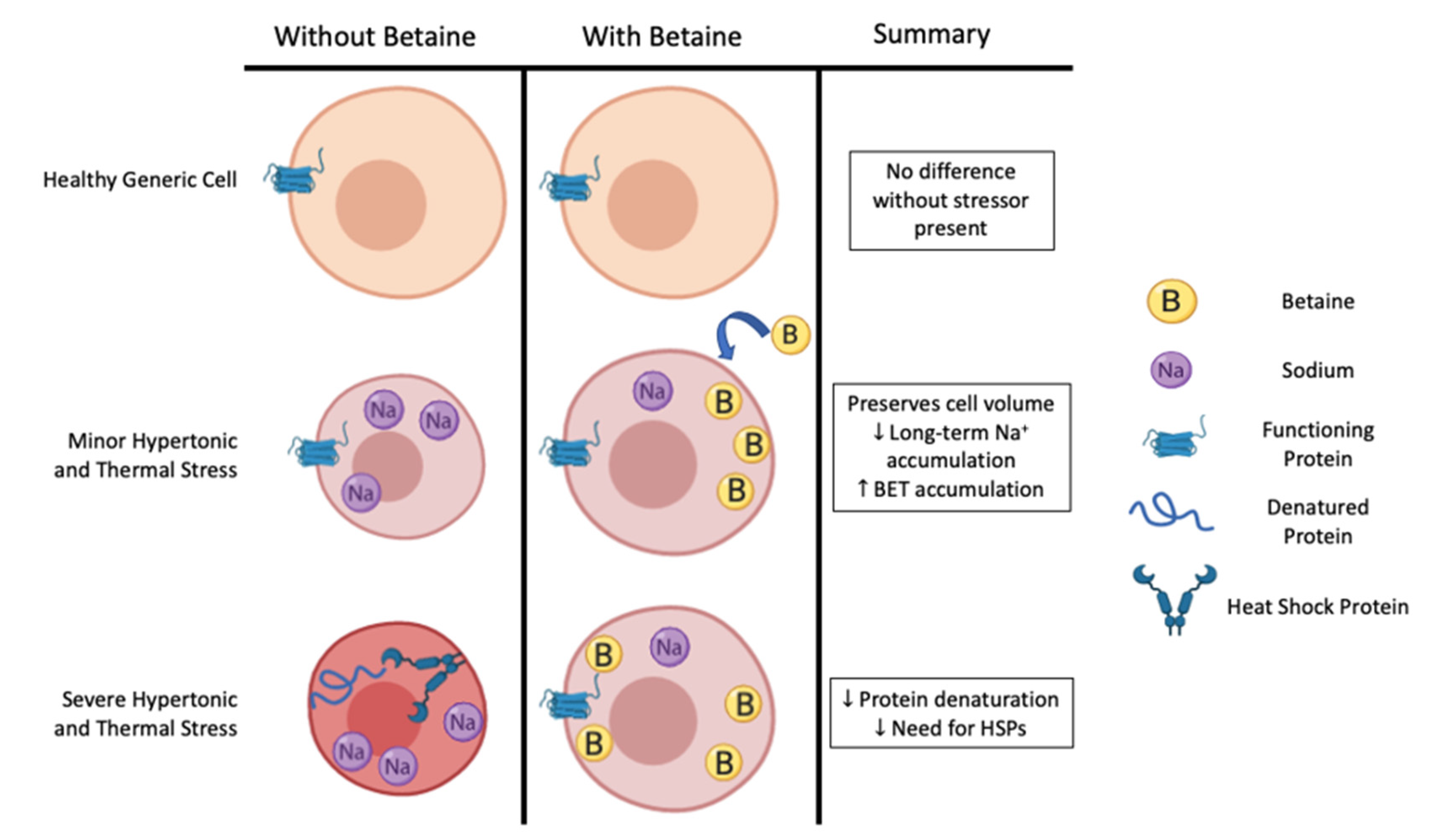
Source: Willingham, B.D., Ragland, T.J. and Ormsbee, M.J. (2020). Betaine Supplementation May Improve Heat Tolerance: Potential Mechanisms in Humans. Nutrients, 12(10), p.2939.
B. Betaine as a “Methyl Donor”
There are thousands of important processes happening in the body to keep it functioning and keep diseases at bay.
One of the key reactions is methylation. As the name implies, this involves the addition of a chemical group called “methyl” groups to various molecules during reactions.
As Betaine has a high content of methyl groups (remember, its chemical name is Tri-methyl glycine) it plays a crucial role in the donation of methyl groups, which are vital for various biochemical reactions in the body.
Through a process called transmethylation, betaine contributes methyl groups to molecules such as homocysteine, facilitating the synthesis of important compounds like methionine and S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe).
This methylation process is essential for proper gene expression, detoxification, neurotransmitter synthesis, and lipid metabolism.

The Health Benefits of Betaine
- Cardiovascular Health
Elevated levels of homocysteine, an amino acid, have been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Betaine acts as a methyl donor and aids in the conversion of homocysteine to methionine, helping to lower homocysteine levels.
By reducing homocysteine, betaine may contribute to the maintenance of cardiovascular health.
This effect comes with a daily intake of 1500mg of Betaine per day in 500mg doses.
- Liver Function
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver. Betaine has shown promise in supporting liver function, particularly in individuals with NAFLD.
Studies have indicated that betaine supplementation may help reduce liver fat accumulation and improve liver enzyme levels.

Source: Wang, C., Ma, C., Gong, L., Dai, S. and Li, Y. (2021). Preventive and therapeutic role of betaine in liver disease: A review on molecular mechanisms. European Journal of Pharmacology, 912, p.174604.
- Cognitive Function
Betaine’s role as a methyl donor is crucial for the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine.
These neurotransmitters play essential roles in mood regulation, cognitive function, and overall mental well-being.
Betaine supplementation has been suggested to support cognitive health, memory, and mood regulation.
- Betaine and digestive support
Betaine HCl is primarily used as a supplement to support digestion.
It is commonly taken before meals to aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients.
Betaine HCl is believed to help increase stomach acid levels, which can be beneficial for individuals with low stomach acid production.

Betaine and Sports Performance
- Power and Strength
Betaine supplementation has demonstrated positive effects on power and strength output.
It may enhance muscular force production and improve performance in high-intensity, short-duration activities.
By increasing power and strength, betaine can be an invaluable aid for athletes and individuals engaged in activities requiring explosive movements.
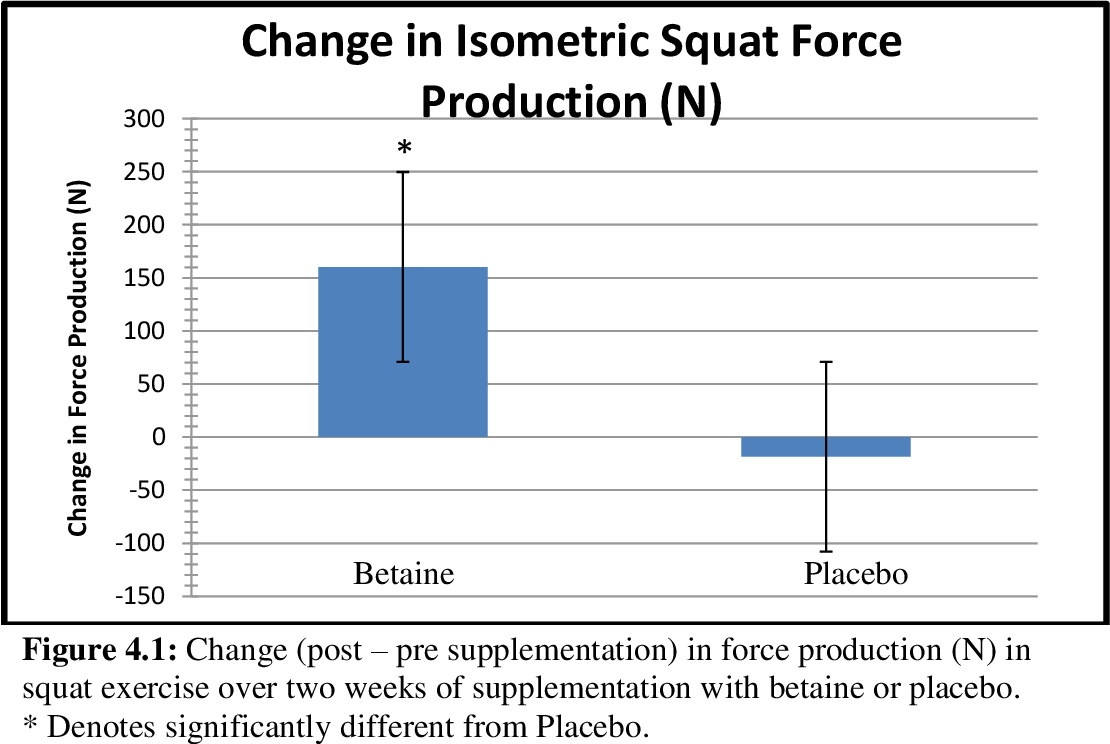
- Endurance Performance
Betaine’s osmolytic properties contribute to maintaining cellular hydration and protecting against exercise-induced dehydration. Adequate hydration is crucial for endurance exercise performance, as dehydration can lead to a decrease in performance and increased fatigue. Betaine supplementation has been shown to improve endurance exercise performance and delay the onset of fatigue.
- Muscle Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is a vital process for muscle growth, repair, and recovery. Betaine supplementation may stimulate muscle protein synthesis, thereby promoting muscle growth and aiding in post-exercise recovery. This effect can be particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals engaged in resistance training.

To view my Professional Profile on LinkedIn: please click here
To see my latest product creations: www.bioteenhealth.com
To view my Scientific Publications on PubMed: please click here
To get in touch, please write to: info@supplementscientist.com
Follow supplementscientist.com on Facebook: please click here
Medical disclaimer
The information presented on this website is intended for adults 18 or over. Its aim is purely educational and does not constitute medical advice. Please consult a medical or health professional before you begin any program related to exercise, nutrition, or supplementation especially if you have a medical condition. If you consume any product mentioned on our site, you do so on your own free will, and you knowingly and voluntarily accept the risks. © 2023. Supplementscientist.com







Leave a Reply